Azure is Microsoft’s cloud computing platform which helps to build solutions to meet business goals. It supports infrastructure (IaaS), platform (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS) computing services. It also supports advanced computing services like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and IoT. Azure allows you to build, manage and deploy the application on a global network.
How does
Azure work?
It is a
private and public cloud platform that helps developers and IT professionals to
build deploy and manage the application. It uses the technology known as
virtualization. Virtualization separates the tight coupling between the
hardware and the operating system using an abstraction layer called a hypervisor.
Hypervisor emulates all the functions of a computer in the virtual machine, it
can run multiple virtual machines at the same time and each virtual machine can
run any operating system such as Windows or Linux. Azure takes this
virtualization technique and repeats it on a massive scale in Datacenter owned
by Microsoft. Each data center has many racks filled with servers and each
server includes the hypervisor to run multiple virtual machines. The network
switch provides connectivity to all those servers.
One server
in each rack runs a special piece of software called fabric controller. Each
fabric controller is connected to another special piece of software known as
the Orchestrator. Each Orchestrator is responsible for managing the work like
responding to user requests.
Microsoft
Azure Services:
The
following are the services that Microsoft Azure offers:
- Compute: It includes Virtual
Machines, Virtual Machine Scale Sets, Functions for serverless computing,
Batch for containerized batch workloads, Service Fabric for microservices
and container orchestration, and Cloud Services for building cloud-based
apps and APIs.
- Networking: With Azure, you can use a
variety of networking tools, like the Virtual Network, which can connect
to on-premise data centers; Load Balancer; Application Gateway; VPN
Gateway; Azure DNS for domain hosting, Content Delivery Network, Traffic
Manager, ExpressRoute dedicated private network fiber connections; and
Network Watcher monitoring and diagnostics.
- Storage: Includes Blob, Queue, File, and
Disk Storage, as well as a Data Lake Store, Backup, and Site Recovery,
among others.
- Web + Mobile: Creating Web + Mobile
applications is very easy as it includes several services for building and
deploying applications.
- Containers: Azure has a property that
includes Container Service, which supports Kubernetes, DC/OS or Docker
Swarm, and Container Registry, as well as tools for microservices.
- Databases: Azure has also included several
SQL-based databases and related tools.
- Data + Analytics: Azure has some big data
tools like HDInsight for Hadoop Spark, R Server, HBase, and Storm
clusters.
- AI + Cognitive Services: With Azure developing
applications with artificial intelligence capabilities, like the Computer
Vision API, Face API, Bing Web Search, Video Indexer, Language
Understanding Intelligent.
- Internet of Things: Includes IoT Hub and IoT
Edge services that can be combined with a variety of machine learning,
analytics, and communications services.
- Security + Identity: Includes Security Center,
Azure Active Directory, Key Vault, and Multi-Factor Authentication
Services.
- Developer Tools: Includes cloud development
services like Visual Studio Team Services, Azure DevTest Labs, HockeyApp
mobile app deployment and monitoring, Xamarin cross-platform mobile
development, and more.
Creation
And Connection of User and Virtual Machine:
Follow the
below steps to create and connect a user to a virtual machine:
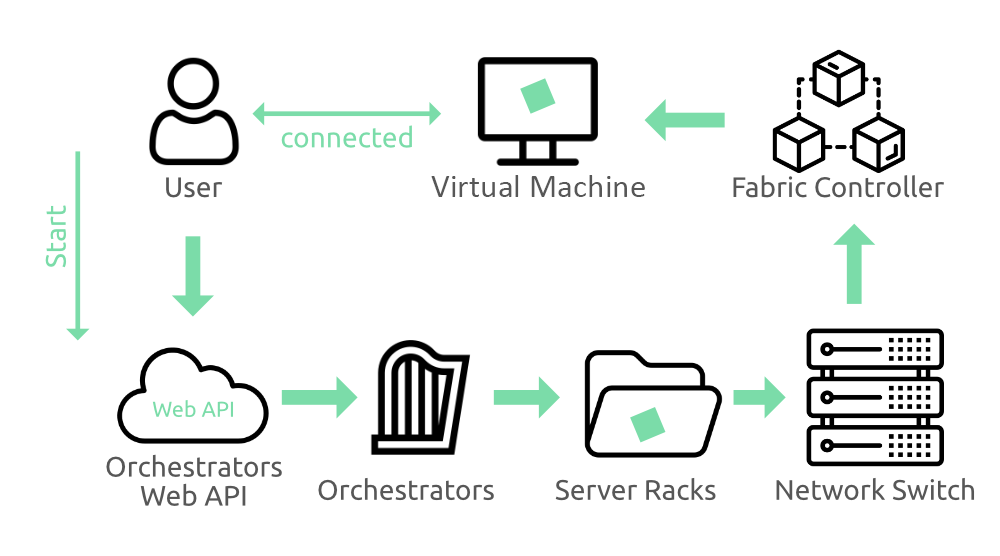
Step 1: The
user makes a request using Orchestrators Web API for creating the virtual
machine.
Step
2: The web API can be called by many tools including the UI of the Azure
portal.
Step 3: The
orchestrator package everything that is needed, it picks the best server
rack and sends the package and request to the fabric controller.
Step
4: Once the fabric controller has created the virtual machine the user can
connect to it.
Advantages
of Azure:
Following
are some advantages of using Microsoft Azure:
- High Availability: It
refers to the quality of computing infrastructure which allows it to
continue functioning, even when some of its components fail.
- Data Security: Azure
provides many of the things to secure data over the cloud-like Microsoft
Defender for Cloud, Key Vault, Azure Information Protection, and many more.
- Scalability: Azure provides
2 types of scalability i.e. Vertical and Horizontal scaling to tackle the
load by changing the capacity of resources or by adding the
resources.
- Cost-Effective: Azure
provides different pricing models that can help to save costs.
- Learning-Curve: Azure
provides various programming languages such as C#, Visual Basics etc., and
tools such as Visual Studio, Azure ML Studio, Azure Dev tools etc., for
learning.
- Hybrid-Capabilities : Azure
provides hybrid working model. It allows the organization or enterprise to
avail services from public cloud as well as from on-premise network.
Disadvantages
of Azure:
Following
are the key disadvantages of using Microsoft Azure:
- Requires Platform Expertise: A
common mistake, on-premise servers compute power does not translate
equivocally in the cloud but can potentially cost businesses.
- Requires Management: As
Azure provides many of the platforms so it needs to be expertly managed
and maintained which includes patching and server monitoring.
- Complexity: For maintaining
the SaaS application for large enterprise, it is bit complexity in nature
to ensure the smoothness of application all the time.


No comments:
Post a Comment