What are Amazon Web Services?
Amazon Web
Services is a subsidiary of Amazon.com that provides on-demand cloud computing
platforms for individuals, companies, and governments, on a paid subscription
basis, pay-as-you-go principle. AWS offers a highly reliable,
scalable, low-cost infrastructure platform in the cloud. You can automate the
infrastructure with the tool called Terraform.
How
Elastic Load Balancing?
The elastic
load balancer is a service provided by Amazon in which the incoming traffic is
efficiently and automatically distributed across a group of backend servers in
a manner that increases speed and performance. It helps to improve the
scalability of your application and secures your applications. Load Balancer
allows you to configure health checks for the registered targets. In case any
of the registered targets. Autoscaling Group fails the health check,
the load balancer will not route traffic to that unhealthy target. Thereby
ensuring your application is highly available and fault tolerant.

Types of
Load Balancers
- Classic Load Balancer: It
is the traditional form of load balancer which was used initially. It
distributes the traffic among the instances and is not intelligent enough
to support host-based routing or path-based routing. It ends up reducing
efficiency and performance in certain situations. It is operated on the
connection level as well as the request level. Classic Load Balancer
is in between the transport layer (TCP/SSL) and the application layer.
- Application Load Balancer: This
type of Load Balancer is used when decisions are to be made related to
HTTP and HTTPS traffic routing. It supports path-based routing and
host-based routing. This load balancer works at the Application layer of
the OSI Model. The load balancer also supports dynamic host port mapping.
- Network Load Balancer: This
type of load balancer works at the transport layer(TCP/SSL) of the OSI
model. It’s capable of handling millions of requests per second. It
is mainly used for load-balancing TCP traffic.
- Gateway Load Balancer: Gateway Load Balancers provide you the facility to deploy, scale, and manage virtual appliances like firewalls. Gateway Load Balancers combine a transparent network gateway and then distribute the traffic.
Steps to
configure an Application load balancer in AWS
Step 1: Launch the two instances on the AWS management console named Instance A and Instance B. Go to services and select the load balancer.
Step 2: Click on Create the load balancer.
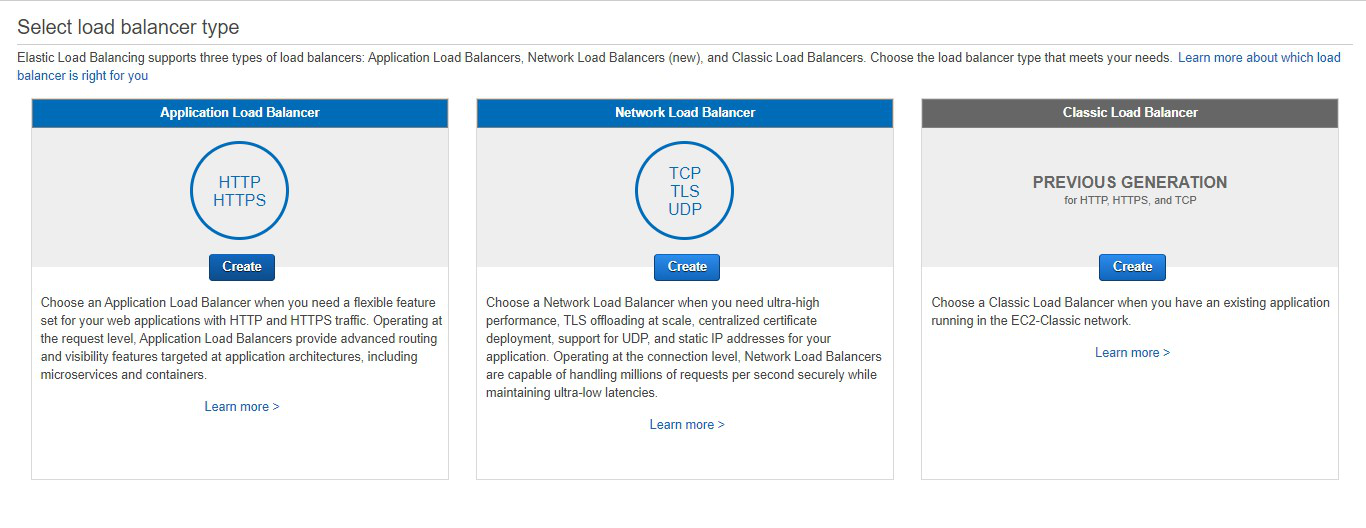
Step 3: Select Application Load Balancer and
click on Create.
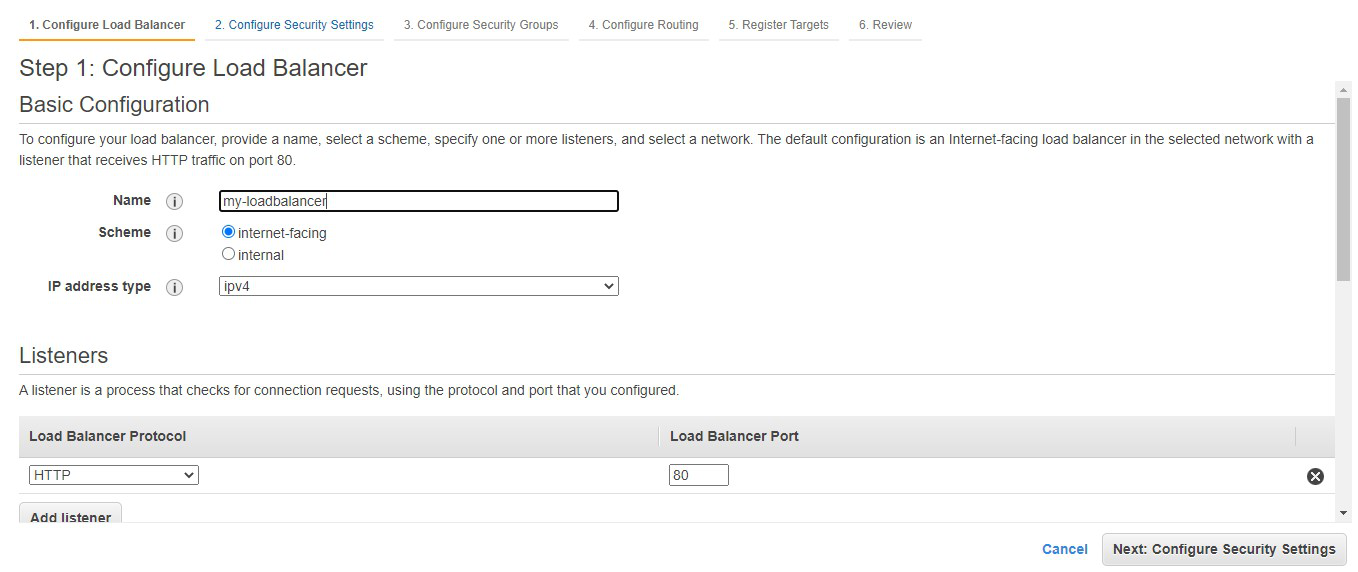
Step 4: Here you are required to configure
the load balancer. Write the name of the load balancer. Choose the scheme as
internet facing.
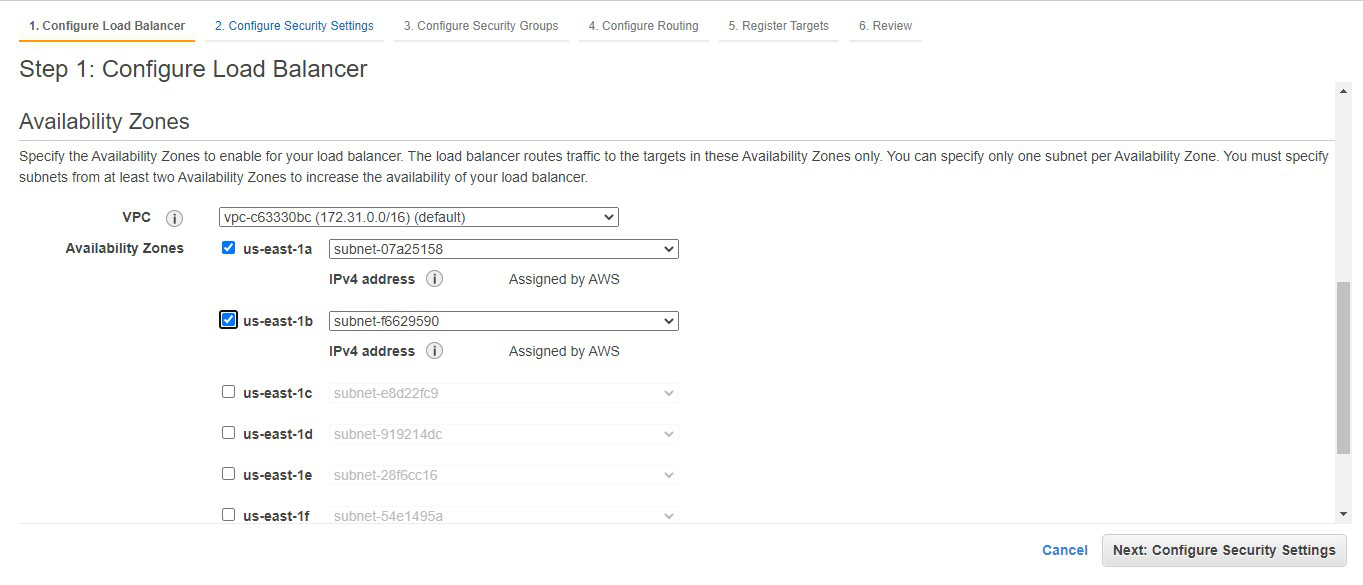
Step
5: Add at least
2 availability zones. Select us-east-1a and us-east-1b
Step
6: We don’t
need to do anything here. Click on Next: Configure Security Groups
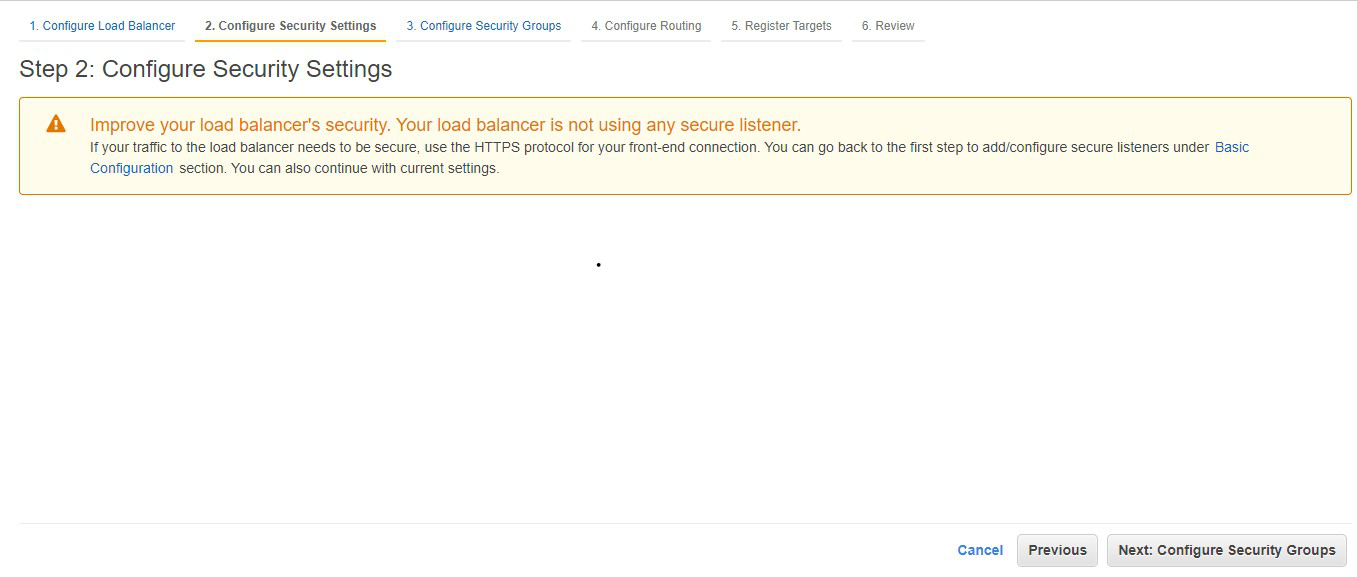
Step 7: Select the default security group.
Click on Next: Configure Routing
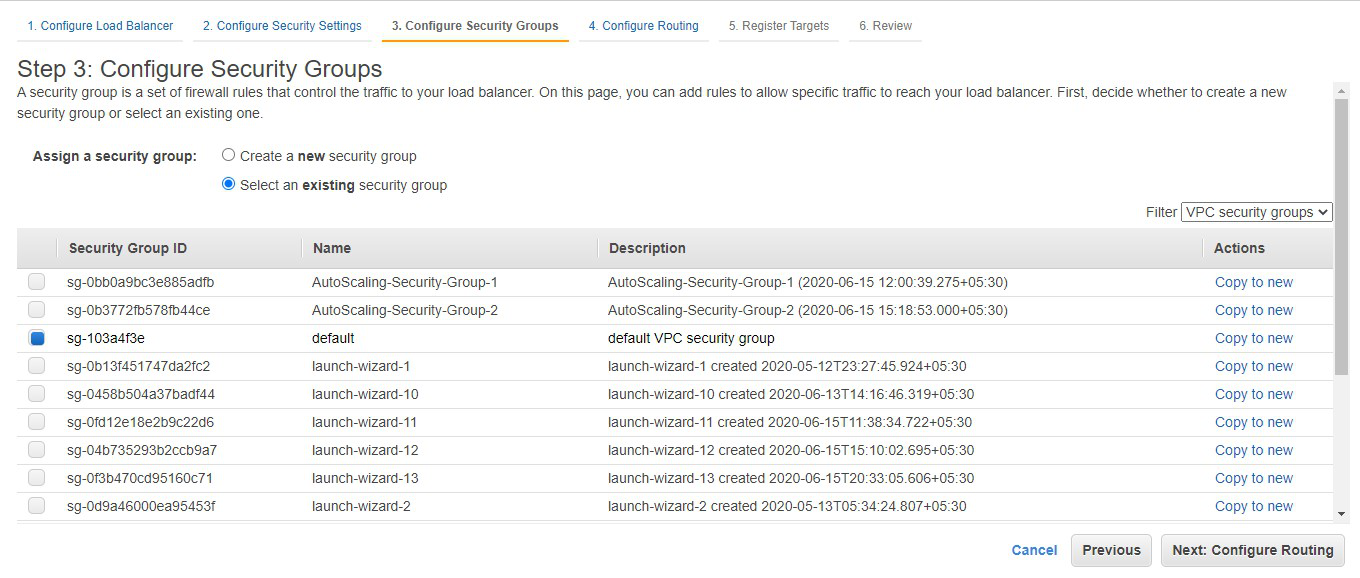
Step 8: Choose the name of the target group
to be my target group. Click on Next: Register Targets.
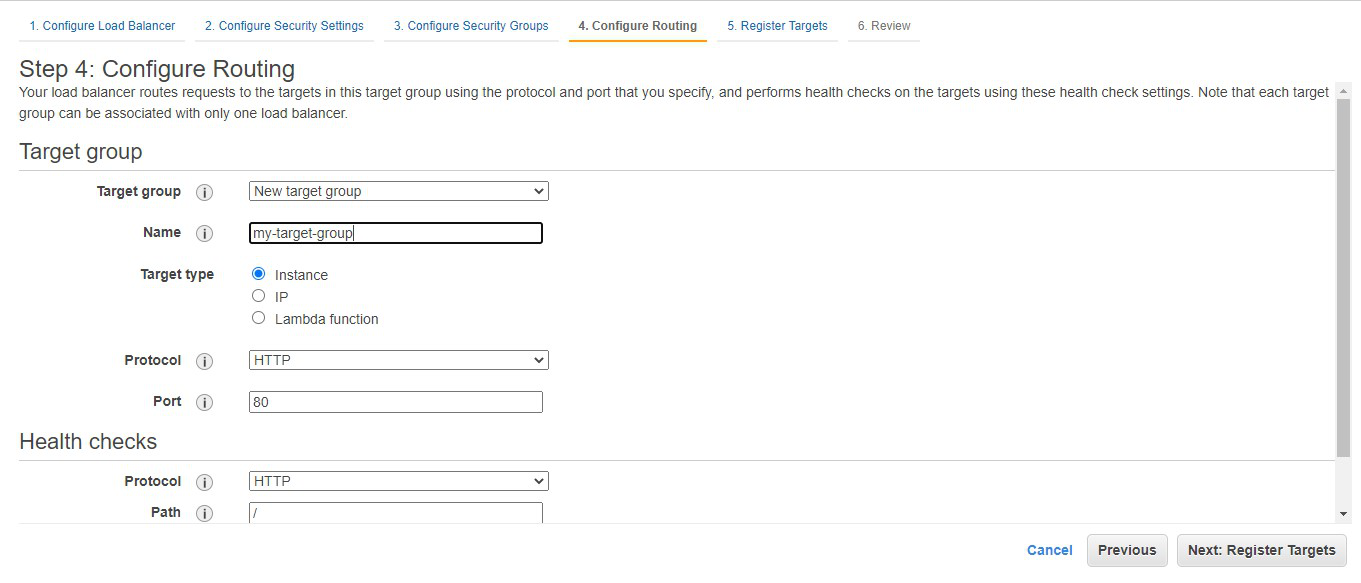
Step 9: Choose instance A and instance B and
click on Add to register. Click on Next: Review.
Step 10: Review all the configurations and
click on create
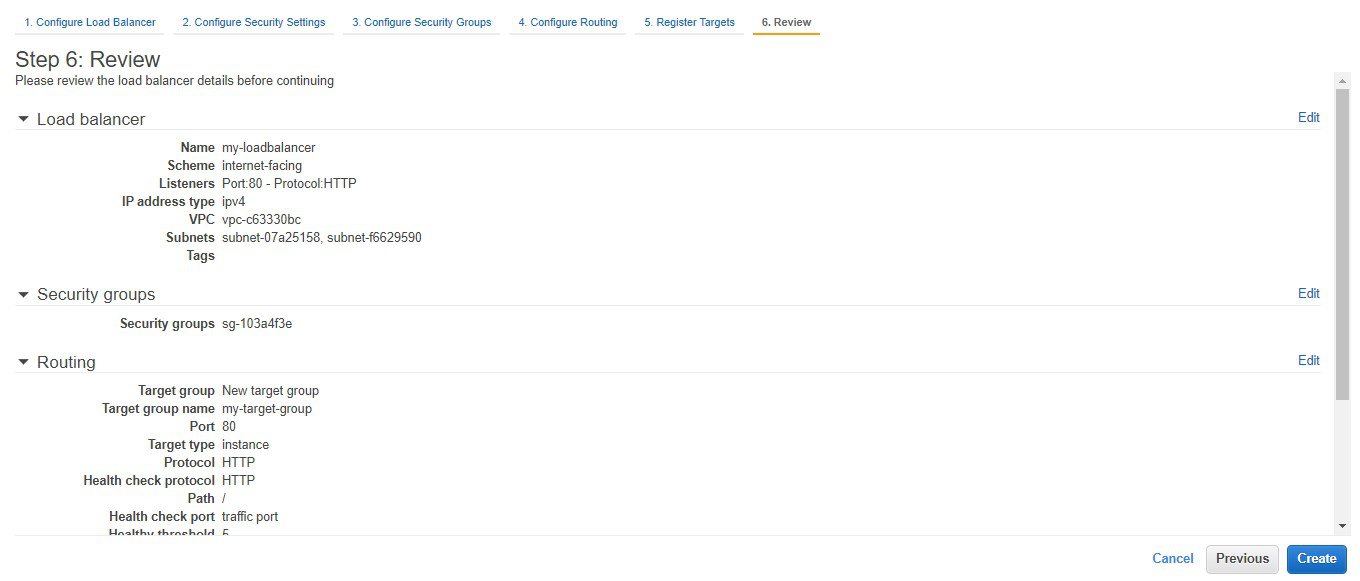
Step 11: Congratulations!! You have successfully created a load balancer. Click on close.
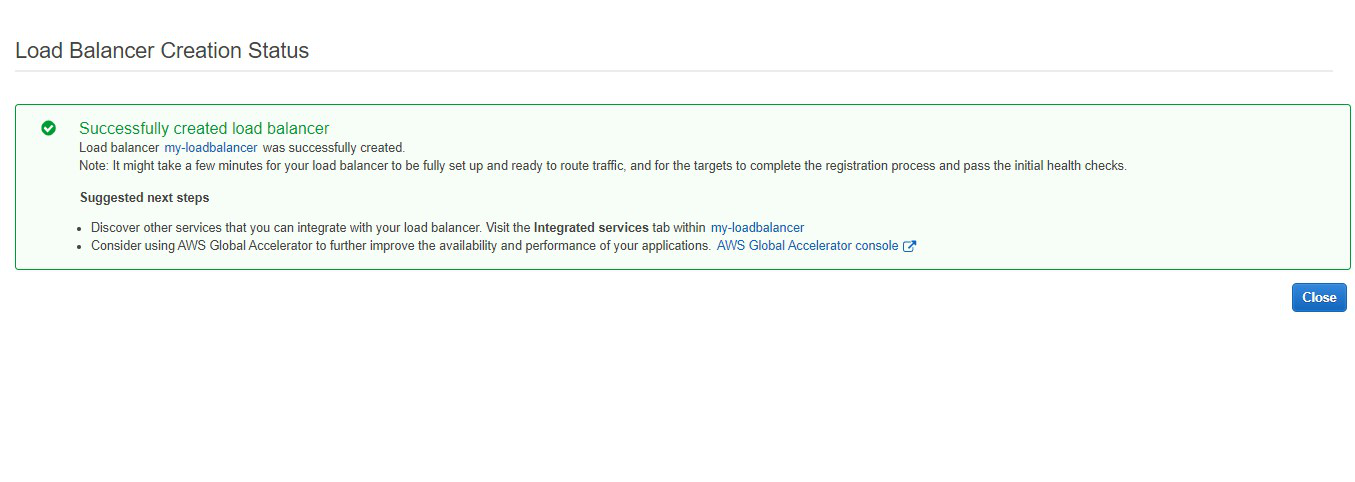
Step
12: This
highlighted part is the DNS name which when copied in the URL will host
the application and will distribute the incoming traffic efficiently between
the two instances.
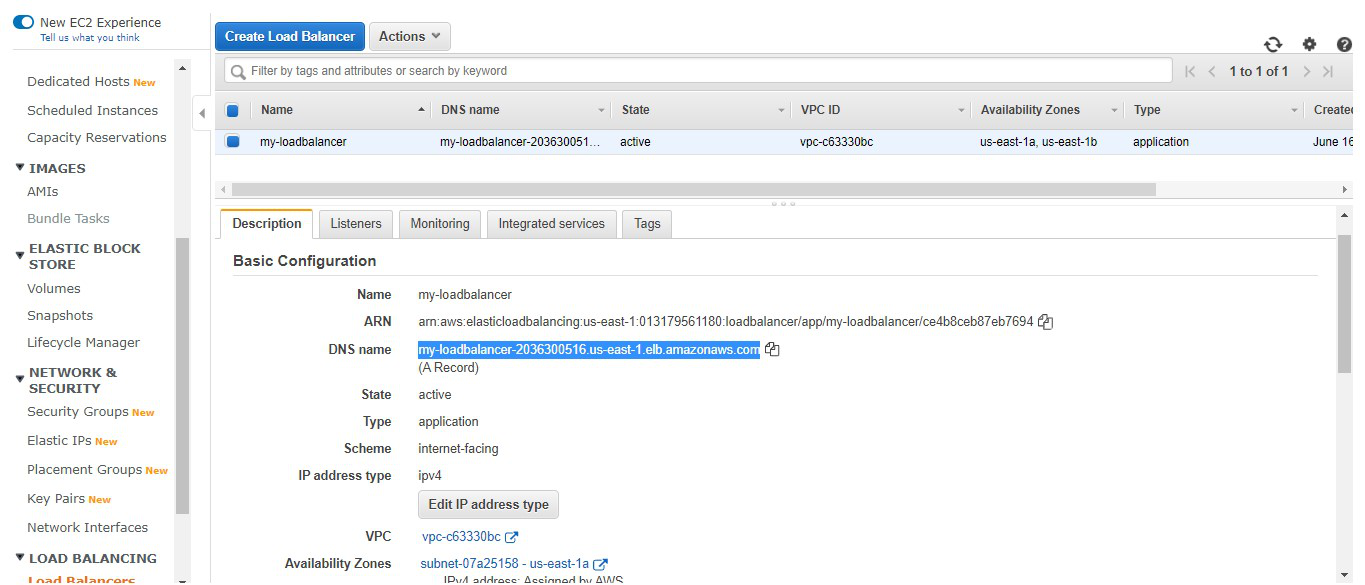
Step 13: This is the listener port 80 which
listens to all the incoming requests
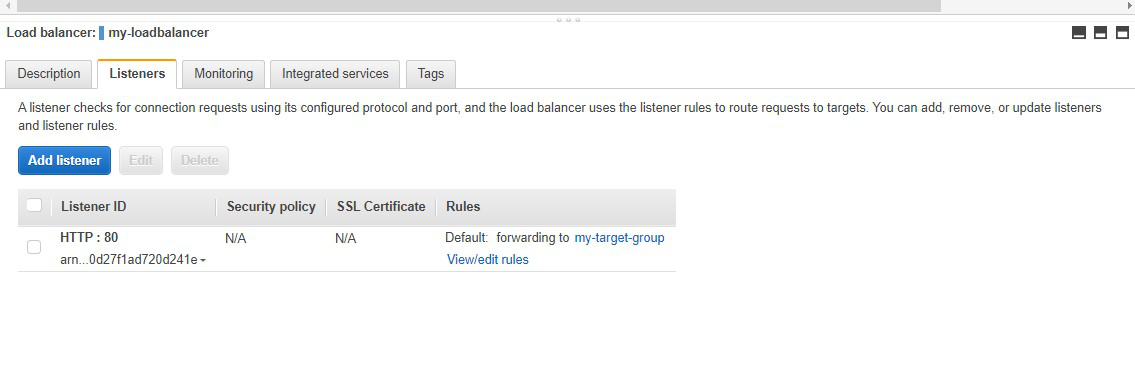
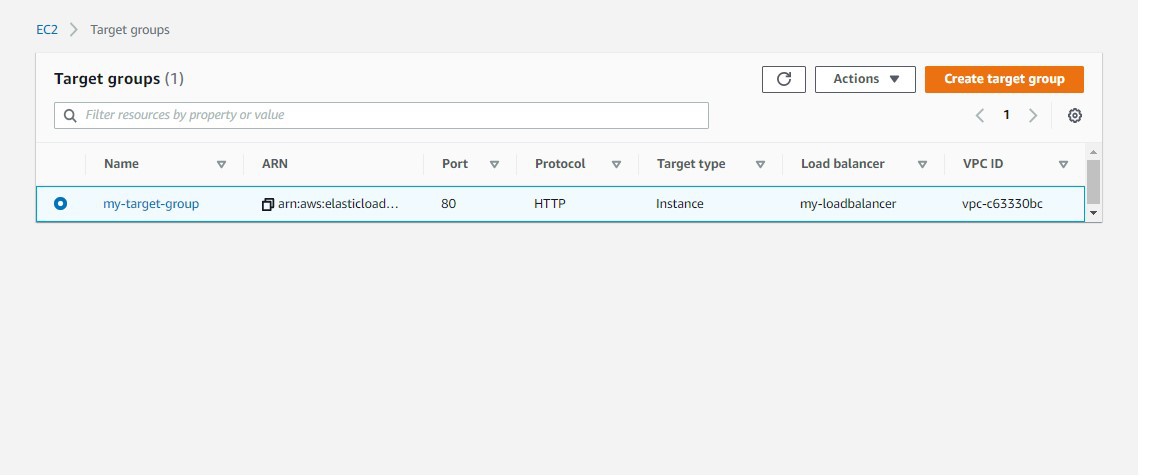
Step
14: This is the
target group that we have created
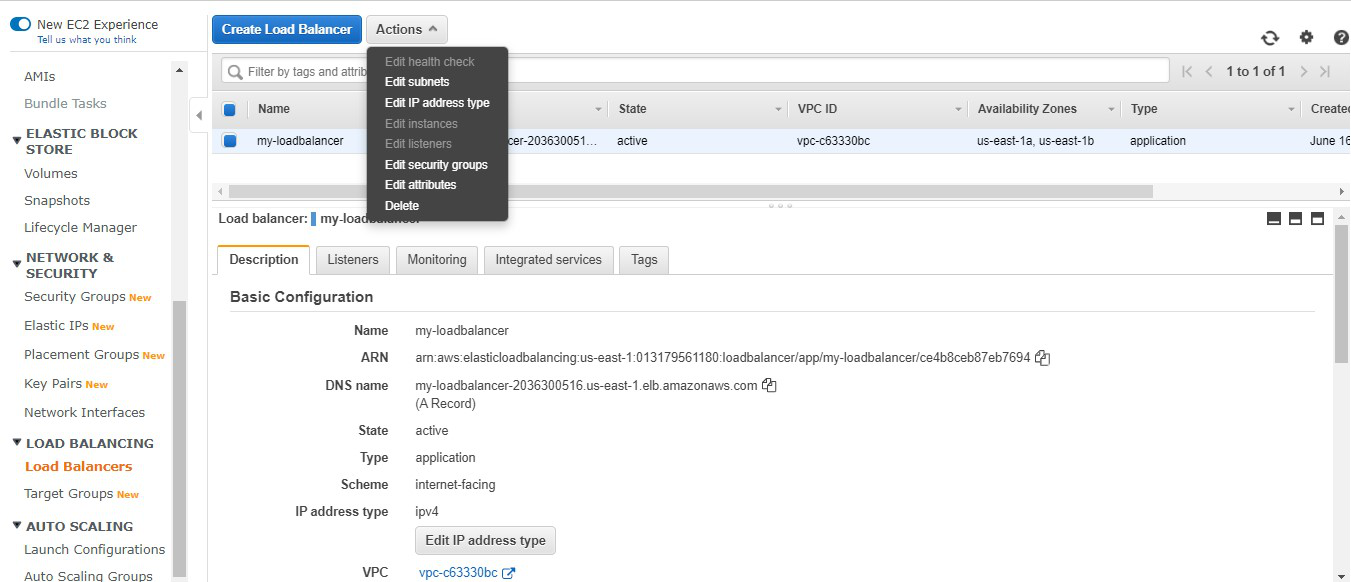
Step 15: Now we need to delete the instance.
Go to Actions -> Click on Delete.
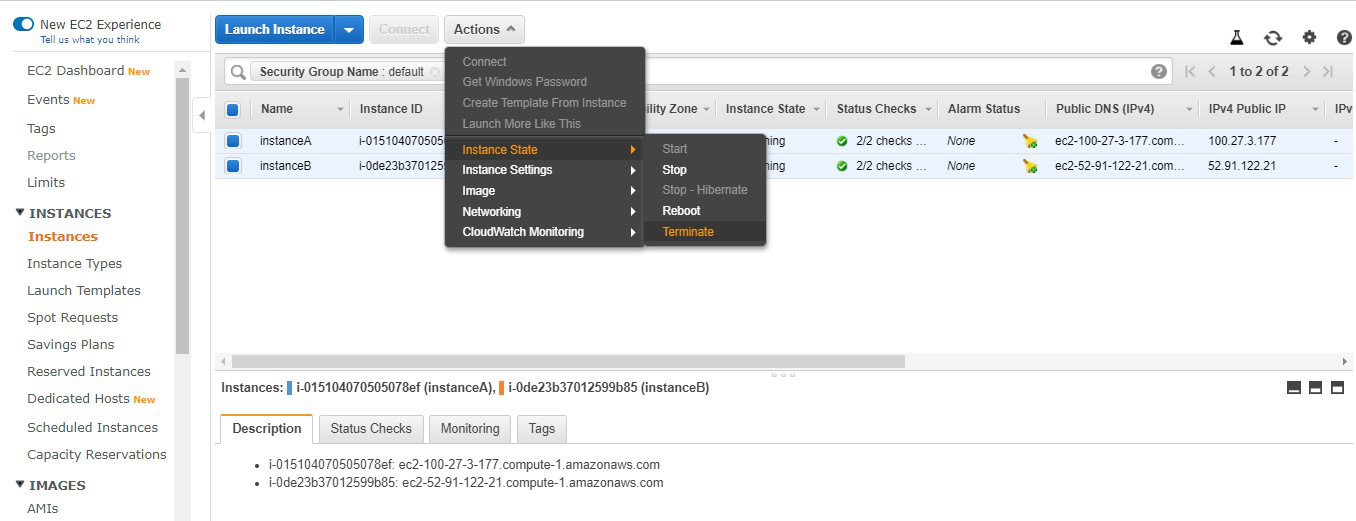
Step 16: Also don’t forget to terminate the
instances.
Features
of cloud
- No up-front investment
- Lowering operating cost
- Highly scalable and efficient
- Easy access
- Reducing business risks and
maintenance expenses
Advantages
of Elastic Load Balancer
- ELB automatically distributes
incoming application traffic across multiple targets, such as EC2,
containers, and IP addresses to achieve high availability.
- It can automatically scale to
handle changes in traffic demand, allowing you to maintain consistent
application performance.
- It can monitor the health of its
registered targets and route traffic only to the healthy targets.
- It evenly distributes traffic
across all availability zones in a region, improving fault tolerance.
Disadvantages
of Elastic Load Balancer
- ELB can add latency to your
application, as traffic must pass through the load balancer before being
routed to your targets.
- It has limited customization
options, so you may need to use additional tools and services to fully
meet your application’s requirements.
- It can introduce
additional complexity to your application architecture, requiring you to
manage and maintain additional resources.
- It can increase your overall AWS
costs, especially if you have high traffic volumes or require multiple
load balancers.


No comments:
Post a Comment