Variables are
an important aspect of any programming language. Without variables, you will
not be able to store any required data. With the help of variables, data is
stored at a particular memory address and then it can be accessed as well as
modified when required. In other words, variables let you store, read, access,
and manipulate data.
Working
of Bash variables
When you
write a bash script, you either want to manipulate the already defined
variable, set the value of the variable, or simply read the predefined
variables. There are various ways to set values of a variable:
1) Directly assigning the value
myvar="Gfg"2) Set its
value in accordance with the value of the result obtained from the program or a
command (Check command substitution topic below)
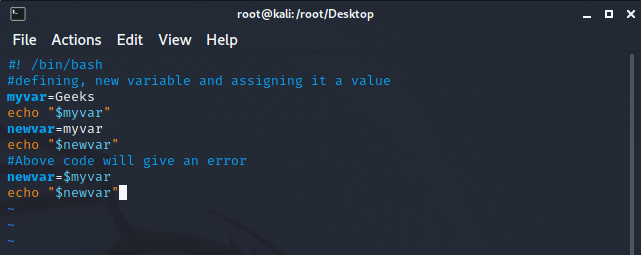
If you are assigning the value of a variable to another variable then use the “$” sign otherwise it will show an error:
Note that
when we define the value of newvar as myvar without the “$” sign it prints the
value as “myvar” rather than getting the value of variable “myvar”.
Output:
Example script:
#! /bin/bash
var1=5
Add () {
var1=$(($var1 + 10))
echo $var1
}
Add
#Assigning the output of function Add to another variable 'var2'.
var2=$var1
echo $var2Output:
15
153) The variable can be read simply by using the $ sign before the variable name. Example:
echo "The value of variable, myvar is $myvar"Now that we
understand how the variables can be read or assigned a value, let us see what
happens after we run the bash script:
- It checks for the variables
which are defined in the script.
- Interprets code line by line.
- It then replaces the variable
names with their assigned values.
- Finally, execute the code line
by line by repeating the above process.
Naming
variables
There are a
few rules to keep in mind while naming a variable:
- Variables can begin with an
alphanumeric character or underscore, followed by a letter, number, or
underscore.
- Variables are case sensitive, so
“gfg” and “Gfg” are two different variables.
- Variables cannot start with a
number.
- Do not use special characters
while defining a variable name.
Example
of rightly defined variable names
gfg
GFG
Gfg
_gfg
g_f_g
March6Examples
of wrongly defined variable names
6March
567
!gfg
@Gfg
gfg*GFgSyntax to
declare the variable or set its value
Declaring or
setting the value of a variable is fairly simple. The basic syntax is as
follows:
variableName=valueExample:
myvar=geeksThere should
not be any space between variable name, equal sign, and the value assigned.
Otherwise, you will encounter an error:
If the value
of the variable contains spaces then use quotes to define them.
myvar="Geeks for geeks"You can also declare a variable using declare command:
declare myvar="geeks"Using
Local and global variables in bash
When you
define a variable in your shell, it is only accessible during that particular
session. Because that is a local variable. In the below example you can see
that when we tried to access the variable “var1” in the new session (session
number-1692), it does not print our variable value.
Note: echo $$ is used to print the process ID of the current session (See special variables below)
To make the variable globally accessible to any child sessions/processes (of the current session), we can make use of the ‘export’ command. Using the export command you can access the variable defined in your previous session in another session as well.
Example:
Let us now
see how to define local and global variables while writing a shell script. It
is no different than any other programming language.
Create a file var.sh, using the command:
touch var.shOpen it in
vim editor using the command:
vim var.shGo to the
insert mode by pressing Esc and ‘i’.
In this
script, we will define a global variable ‘myvar’ and a local variable ‘myvar’.
Then we will try changing the value of the variable ‘myvar’ inside our
function. Finally, we try to call the function and print the value of both the
local variables as well as the global variables. We will see that only the
value of the local variable will be changed.
#! /bin/bash
myvar=5
function calc(){
# use keyword 'local' to define a
# local variable
local myvar=5
(( myvar=myvar*5 ))
# print the value of local variable
echo $myvar
}
# call the function calc
calc
# print the value of global variable and
# observe that it is unchanged.
echo $myvar Save the
file using “:wq!”.
And run it using the command:
bash var.shThe
output:
The first
value which is printed is of our local variable and the second value is of our
global variable which did not change, regardless of the operation we performed
inside the function ‘calc’.
Types of
bash variables
There are
two types of variables in bash:
- The system defined variables or
Environment variables
- User-defined variables
System
defined variables
These are
predefined variables or the variables which are created and maintained by Linux
bash shell. These variables are loaded when you open a new bash session. These
variables are used to define system properties. They are defined in capital
letters. Let’s now see some of the system-defined variables:
- BASH_VERSION
- BASH
- PWD
- OSTYPE
- HOME
- LANG
- HOSTNAME
- PATH
- COLUMNS
- USER
Note: There are more system-defined variables. Above are the common system-defined variables.
You can
see the list of system-defined variables using the following commands:
- set
- env
- printenv
The output
looks like this:
- BASH_VERSION: Displays the name
of your current bash version.
- BASH: Displays the shell name.
- PWD: It stands for “Present
working directory”. It displays the path to your present working
directory.
- OSTYPE: Simply displays the name
of the operating system.
- HOME: Displays the home
directory of the current user.
- LANG: Displays the language of
the Linux system. Example: LANG: en_IN
- HOSTNAME: Displays the name of
the host. Example: kali
- PATH: It displays an ordered
list of paths (separated by colons).
Example:
9. COLUMNS: Displays the length of the column used to show output on the terminal.
10. USER: Displays the current user. Example: root
User-defined
variables
These are
the variables that you define and assign a value.
Syntax:
variable_name=valueExample:
myvar=gfgIf the value
of the variable contains spaces then use quotes to define them.
myvar="Geeks for geeks"Example
script:
- Create a file named – gfg.sh.
- Open the vim editor and go to
the insert mode by pressing Esc and typing ‘i’.
- Write the script:
#! /bin/bash
myvar=Hello
newvar=”welcome to gfg”
echo “$myvar, $newvar”
#variables are case sensitive
Myvar=”Hi again!”
echo “$Myvar”- Save changes by pressing Esc and
“:w”.
- And then quit by pressing Esc
and “:q”.
- Run the script by using the command: “bash gfg.sh"
Note that it is recommended (but not
required) to define your variable in lowercase. To make sure that the defined
variable name doesn’t coincide with the system-defined variable name.
User-defined
variables are deleted after the shell script executes. In contrast,
system-defined variables can be accessed by any other application and are not
stored in any file.
Built-in
special variables
Bash comes
with some built-in special variables. These variables store some important data
that can come in handy when you write a shell script. They are available for
use to all users. Below is the list of these special variables and the result
they store:
| Special variable | Result stored |
|---|---|
| $$ | It represents the process ID of the current shell of the user. Example: 1692 |
| $? | It returns the exit status of the last executed command. Example: 127–> This is the exit status if the command was not found. |
| $0 | It represents the script name. |
| $1-$9 | $1 to $9 represents the 1st to 9th argument passed with the script. |
| ${10}-${n} | It represents the 10th argument to the nth argument passed with the script. |
| $# | It represents the length of any value or the number of arguments passed to the given script. |
| $@ or $* | It represents the list of all arguments that are passed to the script |
Special
variable- $$
This special
variable gives the PID or Process Identifier of the current shell. In the case
of a shell script, it gives the PID under which the script is running.
Special
variable-$?
Every
command returns an exit status. Thus the exit status can be used to identify if
the command is terminated successfully or there was some error.
Some common exit statuses:
| Exit status | Reason |
|---|---|
| 0 | Success |
| 1-255 | Failure |
| 1 | Catchall for general errors |
| 2 | Misuse of shell builtins |
| 13 | Permission denied |
| 126 | Command found but it is not executable |
| 127 | Command not found |
Using
array variables in Bash
Arrays are
used to store data and in bash, you can store values of different types or the
same type in an array.
There are
various ways to declare an array and its elements. In this tutorial, however,
we will declare an array by defining elements that are space-separated.
Syntax:
arrayName=(element1 element2 element3 element4)Note: If
your element includes whitespace then enclose that element in quotes.
Syntax to
get the length of the array:
{#arrayName[@]}Syntax to
get a particular array element:
{arrayName[index]}Syntax to
get the length of a particular array element:
{#arrayName[index]}Example
script:
In this
example, we will write a script to iterate through the array elements, print
their names and respective lengths.
Create a file named “myarray.sh”. Open the file in vim editor.
#! /bin/bash
# declare an array with pre-defined values
declare -a my_data=(Learning "Bash variables" from GFG);
# get length of the array
arrLength=${#my_data[@]}
# print total number of elements in the array
echo "Total number of elements in array is: $arrLength"
# iterate through the array and print length of
# each element and their values
echo "Below are the elements and their respective lengths:"
for (( i=0; i<arrLength; i++ ));
do
echo "Element $((i+1)) is=> '${my_data[$i]}'; and its length is ${#my_data[i]}"
done
# print the whole array at once
echo "All the elements in array : '${my_data[@]}'"Output:
Explicitly
declaring datatype of a variable
In bash, we
do not need to declare data types, like any other programming languages (int,
str, etc..). The data type is identified by the shell script/shell itself (the
variables defined in bash are termed as untyped). But there can be some
circumstances when you will want to explicitly define the data type. In such
cases, you can utilize the declare command to create a variable with a
particular data type. Declare commands offer many flags to explicitly declare
data types.
Below is the list of those flags:

Integer
You can declare an integer using the below command:
declare -i myvarNow that you
defined the data type of variable “myvar” as an integer, if you try assigning
its value as a floating number you will get an error.
Notice that
if you try to assign the value of “myvar” as a string. It evaluates the string
“xyz” as an integer and hence prints 0. Whereas the floating number gives an
error.
Array
Declaring array using flag ‘-a’.
declare -a myarrayor
declare -a myarray=([element1 element2 element3])Associative
array
Declare an associative array using flag ‘-A’
declare -A newArray=([key1]=value1 [key2]=value2 [key3]=value3)Print all
the values of an array using the command:
${newArray[@]}or
${newArray[*]}Example:
Print all
the keys of an array using the command:
${!newArray[@]}or
${!newArray[*]}
To print
both the key, value pair you can use for loop:
# ! /bin/bash
# declare array
declare -A newArray=([Ron]=10 [John]=30 [Ram]=70 [Shyam]=100)
# iterate through the array
for key in "${!newArray[@]}";
do
echo "$key scored : ${newArray[$key]} in Math test";
doneOutput:
Command-line
arguments
Command-line
arguments or positional parameters are used to pass input to a shell script or
a command. Using command-line arguments makes the script more dynamic.
Syntax:
bash script.sh argument1 argument2 argument3 argument4 .......You can pass
in the special variables described above as an argument to your shell script.
Example:
Create a
script named “example1.sh”.
#! /bin/bash
# declare a variable which will store all
# the values of our arguments, in doing so
# we will make use of the special variable
# "$@". Alternatively, "$*" can also be used.
myvar=("$@")
# Lets store the length of the number of arguments
# (currently unknown) in another variable.
# Here we can make use of the special variable '$#'
le="$#"
echo $le
# let us now print the arguments that user
# passed by looping through the length of
# the number of arguments
for (( i=0; i<le; i++ ))
do
echo "Argument $((i+1)) is => ${myvar[i]}"
doneIn the above
script, we made use of special variables “$@” and “$#”.
Let us now
try to make use of other special variables.
Create another script “example2.sh”
#! /bin/bash
echo "The process ID of current shell is: $$"
echo "The exit status of last executed command was: $?"
echo "The name of this script is: $0"
echo "First argument passed to this script is: $1"
echo "Second argument passed to this script is: $2"
echo "Total number of arguments passed to this script is: $#"
echo "His full name is: $1 $2"You can
notice that using command line arguments helps you reduce the number of
variables to be defined in a script.
Command
substitution
Sometimes,
while writing a shell script you will encounter some instances when you want to
assign the output of a particular command to a variable. This can be done with
the help of command substitution. Command substitution typically works by
running a particular shell command and storing its result in a variable for
further use or to display.
Syntax:
varname=`command-name`
Example: myvar=`ls`or
varname=$(command-name)
Example: myvar=$(ls)In the above
examples, the output of the command: ‘ls’ will be stored in the variable
‘myvar’. Let’s now see the output we get after we print the variable ‘myvar’:
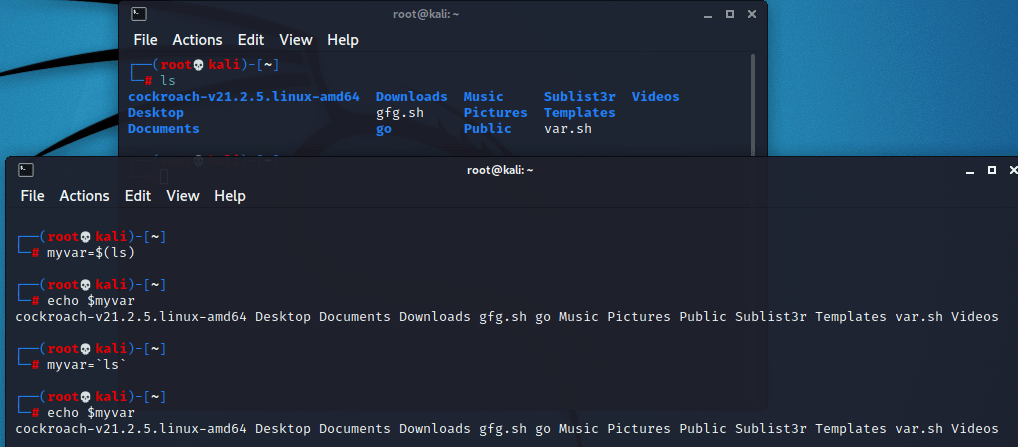
It is evident from the results of the first terminal (i.e by simply running the ‘ls’ command) that the output is extended to multiple lines. Whereas if we use command substitution the output is printed in a single line (space separated) .




















No comments:
Post a Comment